Menu
To provide financial security to the family, earning member insures himself for his life. The insurance company compensates financially to his family on untimely death by discharging a lump sum fund to the dependents. The fund received by the family, against death benefit, depends upon the insurance coverage taken. Hence, the financial security of the family is decided by the insurance coverage adopted. In case of its inadequacy, the family might face financial discomfort. Therefore, determination of the adequacy of coverage value of any life insurance is very important.
Normally the coverage value of life insurance is assessed in the following ways –
The coverage values decided by any of these processes do not follow any structured process to determine precisely the actual fund requirement of the family. So its adequacy, at any point of time, is just a chance. That is why buying a life insurance policy alone is not enough but the adequacy of its coverage also. In absence of any structured process, we might end up with under or over insurance coverage. Over coverage can still be acceptable but under coverage is definitely a point of concern.
In this blog, we shall be discussing the process of determining the coverage value of life insurance.
The life insurance coverage value is dynamic and varies with time. Over a span of 35 years of earning phase, this value keeps on changing from beginning till the end due to continual changes in our financial status and future financial requirements. Therefore, to ensure the death coverage delivering adequate funds, the coverage needs to be aligned to our financial needs, at any given point of time.
The life insurance coverage value is a dynamic value and hence it varies with time. Over a span of 35 years of earning phase, this value keeps on changing from beginning till end. This is because of continual changes in our financial strength and demand to pursue rest of the life. To ensure the ultimate goal i.e. fund value delivered as death benefit needs to match or exceed the demand at that point of time, the coverage value has to be dynamic.
The financial needs to live the rest of the life are influenced by –
The residual liabilities include – any expenditure that will continue after the demise of earning member such as; living expenditure, planned investments to achieve financial targets, other financial deliverables not considered in planning the investments etc. Here, planned investments are considered to be continuing even after the demise of earning member so that the approach adopted to achieve financial targets remain unaffected, only the responsibility shifts from earning member to the corpus received
Savings/ investments are considered as an additional pool of funds as these funds remain available in addition to the fund received against the death benefit. At times, this pool might be capable of discharging a few liabilities on its own. If not, it can reduce the financial burden from the fund received against the death benefit. Thus, at any given point of time, it is the sum of both the funds that discharges all the financial liabilities. As we grow older, we continue delivering our liabilities and creating wealth. As a result, liabilities & the accumulated wealth (i.e. assets), keep on changing with time and makes the required coverage dynamic. For example; after accomplishing the liability of kids’ education, it is eliminated from the residual liabilities and hence fund required to finance remaining liabilities. This aspect must be kept in mind while determining the coverage value of an insurance policy.
This can be better understood by an example-
An individual, aged 40 years, wanted to buy a life insurance policy. His current financials are as follows-
Current assets – The values are the current values based on best estimates –
Current Assets | Purpose |
Investments – 25 Lakh | To build-up a fund for Kid’s Education, Kids’ Wedding & Retirement Corpus |
Provident Fund – 10 Lakh | To finance the post-retirement phase in addition to the Retirement Corpus |
Real Estate – 25 Lakh | For own use |
Bank Balance – 5 Lakh | To handle financial variation |
Gold – 10 Lakh | To handle financial emergencies |
Liabilities – To be delivered over his lifetime
S. No. | Liability Details | Value | Required By | Current Plan |
Liability # 1 | Kids’ Education | |||
1st Kid | Rs. 20 L | 5 Years from now | Planned Investment | |
2nd Kid | Rs. 30 L | 10 Years from now | Planned Investment | |
Liability # 2 | Kids’ Wedding | |||
1st Kid | Rs. 30 L | 10 Years from now | Planned Investment | |
2nd Kid | Rs. 50 L | 15 Years from now | Planned Investment | |
Liability # 3 | Home Loan EMI | Rs. 6000 | Every Month | For next 15 years – deducted from salary |
Liability # 4 | Routine Expenditure | Rs. 40000 | Every Month | Increasing @ 5% PA |
Liability # 5 | Planned Investment | Rs. 40,000 | Every month | Increased @ 8% PA, Expected growth of investment = 8% PA |
Liability # 6 | Retirement Corpus | Rs. 2.5 Cr. | 20 Years from now | Planned Investment |
The insurance coverage value shall be such that it can deliver the death benefit to the extent of residual liabilities, at any point of time. Residual liabilities, towards retirement, become zero when all the liabilities except living expenditure have been delivered. The living expenditure has already planned with retirement corpus. This is applicable for the liabilities to be delivered in the post-retirement phase as these liabilities are also targeted with retirement corpus.
However, in case if the post-retirement phase is not planned through retirement corpus but with other sources of income, the insurance shall continue to finance residual liabilities.
For better understanding the data tabulated above are plotted in graphical form.
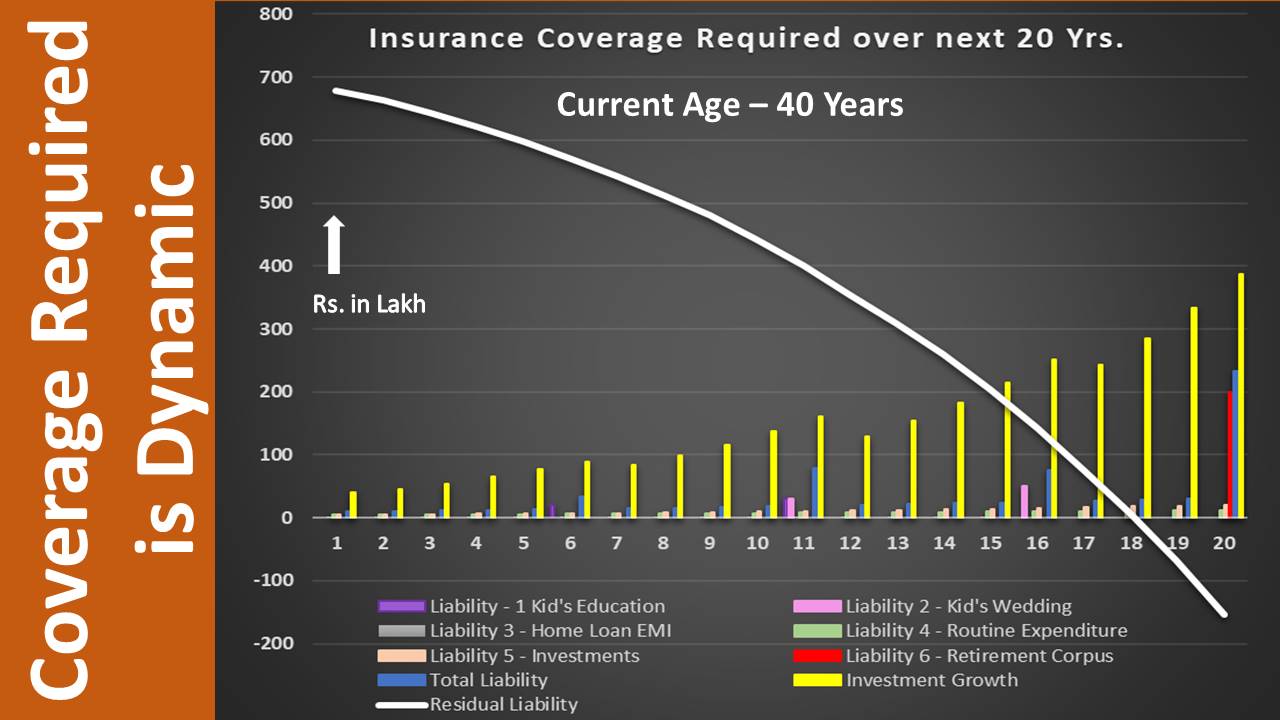
On processing the financial data & representing them in a graphical form reveals the following –
The required insurance coverage keeps on reducing with the delivery of liabilities and increase of savings, investments & its growth. Hence, we need to plan coverage accordingly. In case of undesirable coverage, the additional premium may not give an added advantage. Rather, diverting it towards investment could further reinforce the overall financial strength.
The coverage required after 18 years is negative, including the post-retirement phase. That indicates the fund accumulated is enough to handle all future liabilities, and hence no further insurance coverage is required. can see, the required insurance coverage keeps on reducing with the delivery of liabilities and increase of savings, investments & its growth. The additional premium being paid on account of undesirable coverage can better be used for other purposes. In fact, diverting it towards investment could further re-enforce the overall financial strength.
Conclusion –
The life insurance coverage value plays a very vital role to safeguard a family’s financial security. This, being a personalized value, matching with others is just a coincidence. Therefore, this must be determined based on personal financial data using a structured process. A big coverage does not mean it is adequate unless it commensurate with residual liabilities. Undesirable coverage, on the other hand, does not add any value from the financial security aspect. Thus, diverting such funds towards investment could be a wiser decision to create wealth.
All Rights Reserved By ManishMantra.com